From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Musical note
E
is the third
note
and the fifth
semitone
of the
C major
scale, and
mi
in
fixed-do solfege
. It has
enharmonic
equivalents of
F♭
[(F-flat) which is by definition a diatonic semitone above E
♭
] and
D
 (D-double sharp), amongst others.
(D-double sharp), amongst others.
When calculated in
equal temperament
with a reference of A above middle C as 440
Hz
, the
frequency
of
Middle E
(E
4
) is approximately 329.628 Hz.
[1]
See
pitch (music)
for a discussion of historical variations in frequency.
Designation by octave
[
edit
]
| Scientific
designation
|
Helmholtz
designation
|
Octave name
|
Frequency (Hz)
|
| E
?1
|
E??? or ???E or EEEE
|
Subsubcontra
|
10.301
|
| E
0
|
E?? or ??E or EEE
|
Subcontra
|
20.602
|
| E
1
|
E? or ?E or EE
|
Contra
|
41.203
|
| E
2
|
E
|
Great
|
82.407
|
| E
3
|
e
|
Small
|
164.814
|
| E
4
|
e
′
|
One-lined
|
329.628
|
| E
5
|
e
′
′
|
Two-lined
|
659.255
|
| E
6
|
e
′
′
′
|
Three-lined
|
1318.51
|
| E
7
|
e
′
′
′
′
|
Four-lined
|
2637.02
|
| E
8
|
e
′
′
′
′
′
|
Five-lined
|
5274.041
|
| E
9
|
e
′
′
′
′
′
′
|
Six-lined
|
10548.082
|
| E
10
|
e
′
′
′
′
′
′
′
|
Seven-lined
|
21096.164
|
Scales
[
edit
]
Common scales in the key of E.
[
edit
]
E harmonic minor modes
[
edit
]
- E harmonic minor: E F
♯
G A B C D
♯
E
- E Locrian
♮
6: E F G A B
♭
C
♯
D E
- E Ionian
♯
5: E F
♯
G
♯
A B
♯
C
♯
D
♯
E
- E Dorian
♯
4: E F
♯
G A
♯
B C
♯
D E
- E Phrygian
♮
3: E F G
♯
A B C D E
- E Lydian
♯
2: E F
 G
♯
A
♯
B C
♯
D
♯
E
G
♯
A
♯
B C
♯
D
♯
E
- E Superlocrian bb7: E F G A
♭
B
♭
C D
♭
E
E harmonic major modes
[
edit
]
- E Harmonic Major: E F
♯
G
♯
A B C D
♯
E
- E Dorian
♭
5: E F
♯
G A B
♭
C
♯
D E
- E Phrygian
♭
4: E F G A
♭
B C D E
- E Lydian
♭
3: E F
♯
G A
♯
B C
♯
D
♯
E
- E Mixolydian
♭
2: E F G
♯
A B C
♯
D E
- E Lydian Augmented
♯
2: E F
 G
♯
A
♯
B
♯
C
♯
D
♯
E
G
♯
A
♯
B
♯
C
♯
D
♯
E
- E Locrian
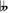 7: E F G A B
♭
C D
♭
E
7: E F G A B
♭
C D
♭
E
F-flat
[
edit
]
F
♭
is a common
enharmonic
equivalent of E, but is not regarded as the same note. F
♭
is commonly found after E
♭
in the same measure in pieces where E
♭
is in the
key signature
, in order to represent a
diatonic
, rather than a chromatic semitone; writing an E
♭
with a following E
♮
is regarded as a chromatic alteration of one scale degree.
References
[
edit
]
See also
[
edit
]